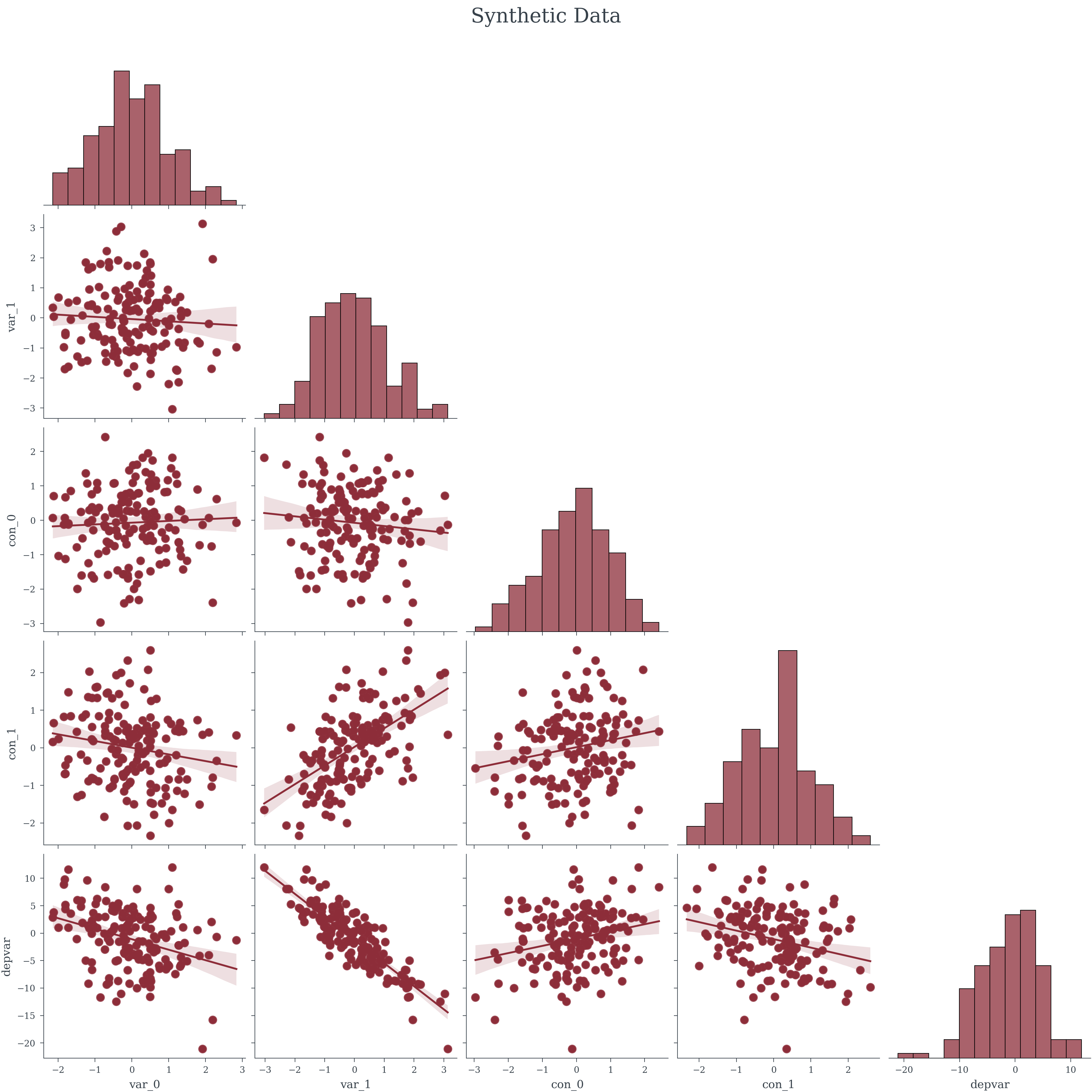
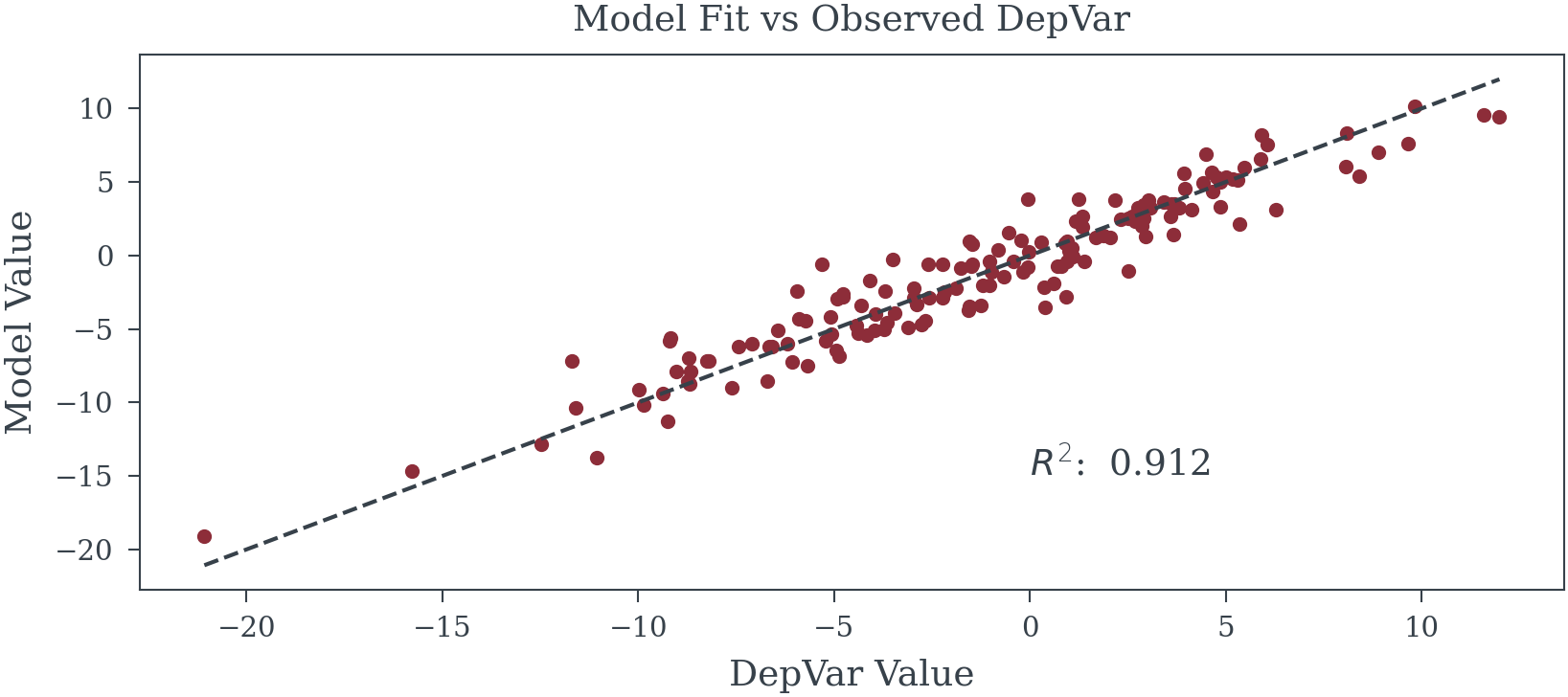
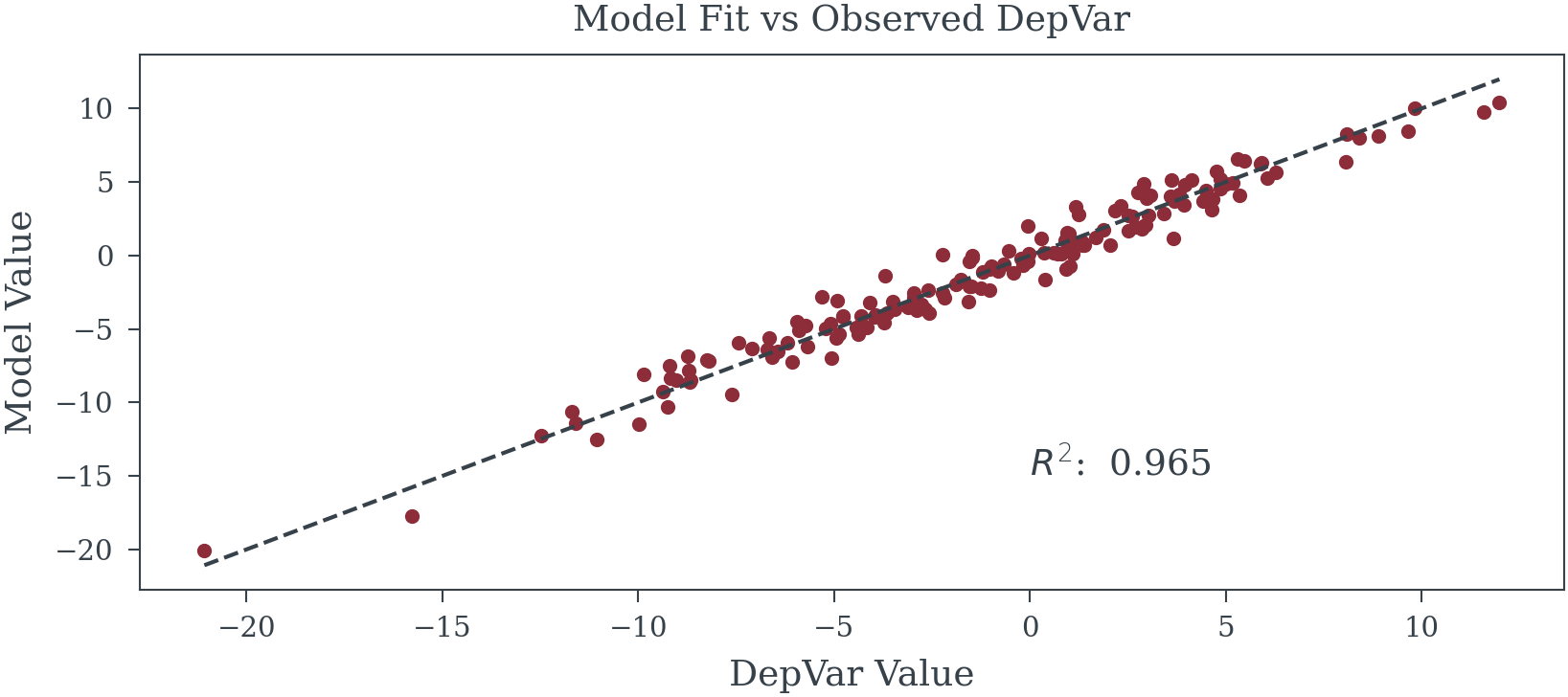
SAMPLE_SIZE = 156
N_INDEPVAR = 2
N_CONFOUNDER = 2
NOISE_SIGMA = 1
RANDOM_SEED = 42
data = generate_ols_data(
SAMPLE_SIZE, N_INDEPVAR,
n_confounder=N_CONFOUNDER,
noise_sigma=NOISE_SIGMA,
random_seed=RANDOM_SEED)
data.head()<xarray.Dataset> Size: 240B
Dimensions: (Index: 5)
Coordinates:
* Index (Index) int64 40B 0 1 2 3 4
Data variables:
var_0 (Index) float64 40B 0.5611 0.9553 -1.824 0.5083 0.162
var_1 (Index) float64 40B -1.173 0.6022 -1.697 -1.17 -1.124
con_0 (Index) float64 40B 1.744 0.828 0.06655 0.9896 0.7824
con_1 (Index) float64 40B 0.439 -0.2966 -0.6974 -1.178 -0.1907
depvar (Index) float64 40B 2.91 -6.19 9.812 2.616 3.067
Attributes:
true_betas: {'var_0': -2.081, 'var_1': -4.826, 'con_0': 0.644, 'con_1': ...
true_alpha: -1.216